Principles of Corrosion
-
-
The types of corrosion include wet corrosion occurring in the presence of moisture and oxygen at room temperature and dry corrosion occurring by the reaction with oxygen due to heating during refining and hot rolling. The majority of the corrosion that usually occurs is wet corrosion.
Principles of Corrosion
1. Wet Corrmosion
Wet corrosion proceeds by an electrochemical reaction. Anode (low potential part) and cathode (high potential part) are formed in the presence of moisture and oxygen, and a local battery is generated between the two electrodes, which accelerates the dissolution oxidation of the metal. In general, unoxidized metals appear to be uniform in texture, but the structure is highly uneven due to thermal and mechanical processing and the addition of various elements. If moisture and oxygen are present on such uneven surfaces, corrosion proceeds by the flow of corrosion current from the anode (low potential part) to the cathode (high potential part).
Anode : Fe → Fe2++2e-
Iron is ionized and dissolved, emitting electrons Cathode: O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-
Cathod : O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-
Fe2+, which is an anode product generating a hydroxyl ion by receiving electrons in the presence of oxygen and moisture, is converted to rust by reaction with OH-, which is a product of cathode, or reaction with moisture.
Fe2++ 2OH- → Fe(OH)2
Fe2++ 2H2O → Fe(OH)2 +2H+
2Fe(OH)2 +¹₂O2 + H2O → 2Fe(OH)3
2Fe(OH)3 → Fe2 O3 + 3H2O
Fe(OH)2, Fe(OH)3, and Fe2O3 that are generated are the major components of red rust.
Like this, wet corrosion is generated as a local battery is generated between the anode (low potential part) and cathode (high potential part), and a corrosion current flows in the presence of moisture and oxygen. The local battery is caused by the contact of dissimilar metals, difference in the oxygen concentration, difference in the liquid temperature, etc.
① Contact of dissimilar metals
Even the same kind of metal is uneven in terms of the structure, a local battery is produced due to a potential difference. If the metal in contact with iron has a higher electric potential than the iron (if the ionization tendency of the contacted metal is low), the iron is ionized and dissolved, emitting electrons.
If the metal in contact with iron has a lower electric potential than the iron (if the ionization tendency of the contacted metal is high), the contacted metal is ionized and dissolved, emitting electrons. For example, when iron and zinc are in contact, zinc is ionized by becoming the anode and corrodes first.
(Anti-corrosion principle of inorganic zinc rich primer) ② Difference in oxygen concentration
A local battery is generated by the oxygen concentration difference on the iron surface. The area with a low oxygen concentration becomes the anode, while the area with a high oxygen concentration becomes the cathode. The area with a low oxygen concentration is ionized and emits electrons. ③ Difference in liquid temperature
A temperature difference occurs in the solution in contact with the iron surface, and a local battery is generated. The area in contact with a high-temperature solution becomes the anode, while the area in contact with a low-temperature solution becomes the cathode. The area in contact with a high-temperature solution is ionized and emits electrons.
In this way, corrosion occurs as corrosion current flows in the presence of moisture and oxygen. The factors that promote this further are salt (sea salt factor), sulfur compounds, and nitrogen compounds. Therefore, depending on the environment where the metal is placed, the rate of corrosion is very different. In general, the corrosion rate of the steel caused by the environment is as follows.
The corrosion rate of the urban environment can be accelerated by air pollution becoming worse each day, and the major causes are the main components of exhaust gas, NOx and SOx. NOx and SOx are combined with atmospheric moisture to form sulfuric acid and nitric acid, which are acidulous. As they are major causes of acid rain, the rate of corrosion increases according to the degree of air pollution. This is even more so in industrial zones.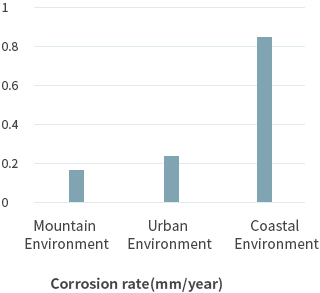
2. Dry Corrosion
The corrosion caused by the reaction between iron and oxygen caused by high-temperature heating during hot rolling at the time of casting steel is called dry corrosion. The rust produced at this time is mill scale that forms a thick iron oxide film.
Mill scale itself has a fine and stable structure in many cases, but cracks and peeling occur easily by impact at the time of molding and repeated cold and warm temperatures. If the steel surface is exposed by cracks and peeling, the mill scale becomes the cathode (high potential part) and the steel becomes the anode (low potential part). Consequently, a local battery is formed easily so that corrosion current flows, and corrosion of the steel proceeds rapidly. Therefore, since even the mill scale that has a stable structure easily peels off and rust proceeds fast, it is necessary to apply anti-corrosive paint after removing it through proper surface treatment.
Especially, if zinc rich paint is used without the sufficient removal of mill scale, it is difficult to expect the anti-corrosive effect by the self-sacrifice method because the zinc rich paint does not directly come into contact with the steel surface.
-